How Much Vitamin D Should Kids Have
How Much Vitamin D Should Kids Have
If you think your child is getting enough vitamin D by just drinking milk, you're probably wrong. Recent studies show that most children aren't getting enough of this essential vitamin.
In October 2014, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) responded by increasing the amount of vitamin D it recommends for children and adolescents.
According the AAP clinical report, Optimizing Bone Health in Children and Adolescents , infants under 12 months require 400 International Units (IU) per day and older children and adolescents require 600 IU per day.
Why Vitamin D?
Common wisdom says that if you're child drinks milk and plays outside, he's getting enough vitamin D, right? Surprisingly, not necessarily.
We know more about vitamin D than we did even five years ago. Because of lifestyle changes and sunscreen usage, the majority of the population shows signs of vitamin D deficiency.Vitamin D helps ensure the body absorbs and retains calcium and phosphorus, both critical for building bone. A vitamin D deficiency can lead to rickets, a bone-softening disease that continues to be reported in the United States mostly in children in the first two years of life. See Vitamin D Deficiency and Rickets for more information.
Vitamin D deficiency also increases the risk of bone fractures in older children, teens, and adults.
The increase in the recommended amount of vitamin D children need each day is a result of new evidence showing its life-long health benefits. Supplementation is important, because most children will not get enough vitamin D through diet alone.
Vitamin D Supplements
It is important that breastfed infants receive an adequate supply of vitamin D through a supplement of 400 IU per day. For formula-fed babies, the requirements are the same. Unless the child is drinking 32 ounces of infant formula per day, a vitamin D supplement is required.If a child or a teenager is not consuming enough vitam in D in his or her diet, a supplement may be needed.
When it comes to giving your child a vitamin D supplement, there's nothing new about the process. Any chewable multivitamin supplement for kids that contains 400 IU of vitamin D is acceptable. There are several liquid vitamin preparations for infants that contain 400 IU vitamin D per dose, as well. Chewable vitamins are generally regarded as safe for children over the age of three who are able to chew hard foods and candy.
For breast or bottle-fed babies: Liquid supplements are the best option. There are liquid preparations that give the recommended intake of 400 IU in ½ or 1 mL. There are also liquid drop solutions available that provide one drop that equals 400 IU per day.
As with all medications and supplements, vitamin D supplements should be kept out of a child's reach.
Finding Vitamin D Naturally
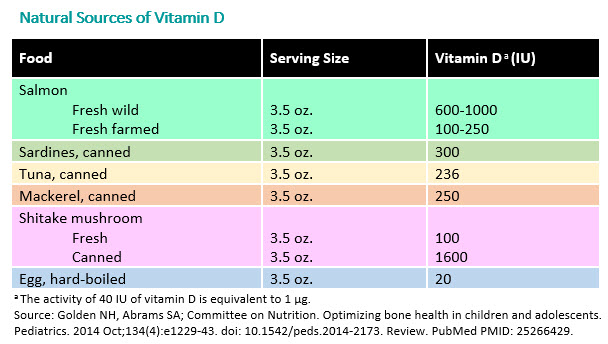
In addition to vitamin supplements, enriched foods are another way to increase the vitamin D in your child's diet. Look for foods fortified with vitamin D such as milk, cereal, orange juice, yogurt, and margarine. Vitamin D is found naturally in only a few foods. See natural sources listed in the chart below.
Quick Tips: The ABCs of Vitamin D
How to make sure your child is getting enough vitamin D:
-
Breastfed and partially breastfed infants should be supplemented with 400 IU a day of vitamin D beginning in the first few days of life.
-
All non-breastfed infants, as well as older children, who are consuming less than 32 ounces per day of vitamin D-fortified formula or milk, should receive a vitamin D supplement of 400 IU a day.
-
Adolescents who do not get 600 IU of vitamin D per day through foods should receive a supplement containing that amount.
-
Children with an increased risk of vitamin D deficiency, such as those taking certain medications and with chronic diseases such as cystic fibrosis, may need higher doses of vitamin D. Consult your pediatrician.
Additional Information:
-
Vitamin D & Iron Supplements for Babies: AAP Recommendations
-
Vitamin D and Sun Exposure
-
Where We Stand: Vitamins
-
Calcium: The Teen Bone Builder
-
Calcium and Vitamin D Requirements of Enterally Fed Preterm Infants (AAP Clinical Report) – Includes dietary recommendations for vitamin D and calcium intakes specifically for preemies
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
How Much Vitamin D Should Kids Have
Source: https://www.healthychildren.org/English/healthy-living/nutrition/Pages/Vitamin-D-On-the-Double.aspx

Leave a Comment